Abstract
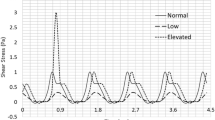
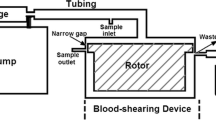
The mechanisms underlying shear stress-induced platelet aggregation (SIPA) were investigated by measuring changes in the platelet size distributions resulting from the exposure of human platelet-rich plasma (PRP) to well-defined shear stresses in a modified viscometer. Exposure of PRP to a shear stress of 100 dyne/cm2 for 1 min at 37°C resulted in the loss of single platelets, an overall shift in the distribution to larger particle sizes, and the generation of platelet fragments. Treatment of PRP prior to shearing with a monoclonal antibody directed against platelet glycoprotein (GP) IIb-IIIa (integrin αIIbβ3) at a concentration that completely inhibited ADP-induced platelet aggregation also inhibited SIPA. Furthermore, incubation of PRP with a recombinant fragment of von Willebrand factor (vWF) that abolishes ristocetin-induced platelet agglutination significantly inhibited but did not eliminate SIPA. Pretreatment of PRP with the tetrapeptides RGDS or RGDV, which constitute the GP IIb-IIIa peptide recognition sequences on fibrinogen and vWF, almost completely blocked platelet aggregation at 100 dyne/cm2, whereas the negative control peptide RGES had no discernible effect. Finally, incubation of PRP with a monoclonal antibody directed against the platelet vitronectin receptor (integrin αvβ3) did not affect SIPA. These results indicate that both GP IIb-IIIa and GP Ib, the latter through its interaction with vWF, are required for SIPA at 100 dyne/cm2; that the interaction of GP IIb-IIIa with its adhesive ligands under shear stress can be inhibited by RGD-containing peptides; and that the vitronectin receptor on platelets, which shares the same β3 subunit as GP IIb-IIIa, plays no role in SIPA. On the basis of these results, the assessment of platelet size distributions provides a sensitive and quantitative measurement for the study of SIPA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baumgartner, H. R., T. B. Tschopp, and D. Meyer. Shear rate-dependent inhibition of platelet adhesion and aggregation to collagenous surfaces by antibodies to human factor VIII/von Willebrand factor.Br. J. Haematol. 44:127–139, 1980.
Baumgartner, H. R., V. T. Turitto, and H. J. Weiss. Effects of shear rate on platelet interaction with subendothelium in citrated and native blood. II. Relationships among platelet adhesion, thrombus dimensions, and fibrin formation.J. Lab. Clin. Med. 95:208–221, 1980.
Brown, C. H., L. B. Leverett, C. W. Lewis, C. P. Alfrey, and J. D. Hellums. Morphological, biochemical, and functional changes in human platelets subjected to shear stress.J. Lab. Clin. Med. 86:462–471, 1975.
Caen, J. P., A. T. Nurden, C. Jeanneau, H. Michel, G. Tobelem, S. Levy-Toledano, Y. Sultan, F. Valensi, and J. Bernard. Bernard-Soulier syndrome: A new platelet glycoprotein abnormality. Its relationship with platelet adhesion to subendothelium and with the factor VIII/von Willebrand protein.J. Lab. Clin. Med. 87:586–596, 1976.
Chow, T. W., J. D. Hellums, J. L. Moake, and M. H. Kroll. Shear stress-induced von Willebrand factor binding to platelet glycoprotein Ib initiates calcium influx associated with aggregation.Blood 80:113–120, 1992.
DeMarco, L., A. Girolami, T. S. Zimmerman, and Z. Ruggeri. von Willebrand factor interaction with the glycoprotein II/IIIa complex: Its role in platelet function as demonstrated in patients with congenital afibrinogenemia.J. Clin. Invest. 77:1272–1277, 1986.
Gemmell, C. H., M. V. Sefton, and E. L. Yeo. Plateletderived microparticle formation involves glycoprotein IIb-IIIa.J. Biol. Chem. 268:14586–14589, 1993.
Gralnick, H. R., S. Williams, L. McKeown, W. Kramer, H. Krutzsch, M. Gorecki, A. Pinet, and L. I. Garfinkel. A monomeric von Willebrand factor fragment, Leu-504-Lys728, inhibits von Willebrand factor interaction with glycopotein Ib-IX.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89:7880–7884, 1992. Erratum appears inProc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90(7): 3118, 1993.
Ikeda, Y., M. Handa, K. Kawano, T. Kamata, M. Murata, Y. Araki, H. Anbo, Y. Kawai, K. Watanabe, I. Itagaki, K. Sakai, and Z. Ruggeri. The role of von Willebrand factor and fibrinogen in platelet aggregation under varying shear stress.J. Clin. Invest. 87:1234–1240, 1991.
Kroll, M. H., J. D. Hellums, Z. Guo, W. Durante, K. Razdan, J. K. Hrbolich, and A. I. Schafer. Protein kinase C is activated in platelets subjected to pathological shear stress.J. Biol. Chem. 268:3520–3524, 1993.
Lawrence, J. B., W. S. Kramer, L. P. McKeown, S. B. Williams, and H. R. Grainick. Arginine-glycine-aspartic-acid-and fibrinogen γ-chain carboxyterminal peptides inhibit platelet adherence to arterial subendothelium at high wall shear rates.J. Clin. Invest. 86:1715–1722, 1990.
Meyer, D., and H. R. Baumgartner. Role of von Willebrand factor in platelet adhesion to the subendothelium.Br. J. Haematol. 54:1–9, 1983.
Moake, J. L., N. A. Turner, N. A. Stathopoulos, L. H. Nolasco, and J. D. Hellums. Involvement of large plasma von Willebrand factor (vWF) multimers and unusually large vWF forms derived from endothelial cells in shear stressinduced platelet aggregation.J. Clin. Invest. 78:1456–1461, 1986.
Moake, J. L., N. A. Turner, N. A. Stathopoulos, L. H. Nolasco, and J. D. Hellums. Shear-induced platelet aggregation can be mediated by vWF released by platelets, as well as exogenous large or unusually large vWF multimers, requires adenosine diphosphate, and is resistant to aspirin.Blood 71:1366–1374, 1988.
Peterson, D. M., N. A. Stathopoulos, T. D. Giorgio, J. D. Hellums, and J. L. Moake. Shear-induced platelet aggregation requires von Willebrand factor and platelet membrane glycoproteins Ib and IIb-IIIa.Blood 69:625–628, 1987.
Phillips, D. R., I. F. Charo, and R. M. Scarborough. GP IIb-IIIa: The responsive integrin.Cell 65:359–362, 1991.
Ruggeri, Z. M. The platelet glycoprotein Ib-IX complex. In:Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis, edited by B. S. Coller. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders, 1990, pp. 35–68.
Sixma, J. J., and J. Wester. The hemostatic plug.Sem. Hematol. 14:265–299, 1977.
Timmons, S., and J. Hawiger. von Willebrand factor can substitute for plasma fibrinogen in ADP-induced platelet aggregation.Trans. Assoc. Am. Physicians 99:226–235, 1986.
Turitto, V. T., H. J. Weiss, and H. R. Baumgartner. Decreased platelet adhesion on vessel segments in von Willebrand's disease: A defect in initial platelet attachment.J. Lab. Clin. Med. 102:551–564, 1983.
Walsh, P. N. Platelets, blood coagulation, and hemostasis. In:Platelets and Thrombosis, edited by S. Sherry and A. Scriabine. Baltimore: University Park, 1972, pp. 23–43.
Weiss, H. J., J. Hawiger, Z. M. Ruggeri, V. T. Turitto, P. Thiagarajan, and T. Hoffmann. Fibrinogen-independent platelet adhesion and thrombus formation on subendothelium mediated by glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex at high shear rate.J. Clin. Invest. 83:288–297, 1989.
Weiss, H. J., V. T. Turitto, and H. R. Baumgartner. Effect of shear rate on platelet interaction with subendothelium in citrated and native blood. I. Shear-rate dependent decrease of adhesion in von Willebrand's disease and the Bernard-Soulier syndrome.J. Lab. Clin. Med. 92:750–764, 1978.
Weiss, H. J., V. T. Turitto, and H. R. Baumgartner. Platelet adhesion and thrombus formation on subendothelium in platelets deficient in glycoproteins IIb-IIIa, Ib and storage granules.Blood 67:322–330, 1986.
Weiss H. J., V. T. Turitto, and H. R. Baumgartner. Role of shear rate and platelets in promoting fibrin formation on rabbit subendothelium.J. Clin. Invest. 78:1072–1082, 1986.
Zwaal, R. F. A., P. Comfurius, and E. M. Bevers. Platelet procoagulant activity and microvesicle formation: Its putative role in hemostasis and thrombosis.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1180:1–8, 1992.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Slack, S.M., Jennings, L.K. & Turitto, V.T. Platelet size distribution measurements as indicators of shear stress-induced platelet aggregation. Ann Biomed Eng 22, 653–659 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02368290
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02368290