Abstract
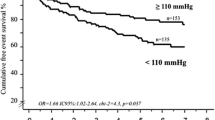
High systolic blood pressure (SBP) has been linked to worse cardiovascular outcomes. However, emerging data suggest that in patients with heart failure (HF), low SBP correlates with increased mortality. The purpose was to examine the impact of baseline and post-exercise systolic and diastolic blood pressure (DBP), as well as pulse pressure (PP), on cardiac mortality in patients with systolic HF. One hundred sixty patients with systolic HF (left ventricular ejection fraction 33 ± 8) were studied. Blood pressure (BP) levels were determined at rest and at peak exercise during a cardiopulmonary exercise test. Patients were followed up for a period of 2.5 ± 0.8 years. During this period 22 patients died and 5 subjects underwent heart transplantation. Patients with higher SBP and DBP at rest, and patients with SBP ≥160 mmHg and PP ≥75 mmHg at peak exercise had the most favorable prognosis. There was a fourfold increase in cardiac mortality risk for patients with SBP <160 mmHg at peak exercise (hazard ratio: 3.97, 95% confidence interval: 1.60–9.84) and a threefold increase for patients with PP <75 mmHg at peak exercise (hazard ratio: 2.96, 95% confidence interval: 1.29–6.82). There is an inverse relationship between SBP and cardiac mortality in patients with systolic HF. BP response to exercise could serve as a simple risk stratification model in HF patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jessup M, Brozena S (2010) Elevated troponin T on discharge predicts poor outcome of decompensated heart failure. Heart Vessels 25:217–222
Darne B, Girerd X, Safar M, Cambien F, Guize L (1989) Pulsatile versus steady component of blood pressure: a cross-sectional analysis and a prospective analysis on cardiovascular mortality. Hypertension 13:392–400
Franklin SS, Khan SA, Wong ND, Larson MG, Levy D (1999) Is pulse pressure useful in predicting risk for coronary heart disease? The Framingham heart study. Circulation 100:354–360
Benetos A, Safar M, Rudnichi A, Smulyan H, Richard JL, Ducimetieere P, Guize L (1997) Pulse pressure: a predictor of long-term cardiovascular mortality in a French male population. Hypertension 30:1410–1415
Fang J, Madhavan S, Cohen H, Alderman MH (1995) Measures of blood pressure and myocardial infarction in treated hypertensive patients. J Hypertens 13:413–419
Chae CU, Pfeffer MA, Glynn RJ, Mitchell GF, Taylor JO, Hennekens CH (1999) Increased pulse pressure and risk of heart failure in the elderly. JAMA 281:634–639
Vaccarino V, Holford TR, Krumholz HM (2000) Pulse pressure and risk for myocardial infarction and heart failure in the elderly. J Am Coll Cardiol 36:130–138
Chrysohoou C, Pitsavos C, Barbetseas J, Kotroyiannis I, Brili S, Vasiliadou K, Papadimitriou L, Stefanadis C (2009) Chronic systemic inflammation accompanies impaired ventricular diastolic function, detected by Doppler imaging, in patients with newly diagnosed systolic heart failure (Hellenic Heart Failure Study). Heart Vessels 24:22–26
Mancia G, Laurent S, Agabiti-Rosei E, Ambrosioni E, Burnier M, Caulfield MJ, Cifkova R, Clément D, Coca A, Dominiczak A, Erdine S, Fagard R, Farsang C, Grassi G, Haller H, Heagerty A, Kjeldsen SE, Kiowski W, Mallion JM, Manolis A, Narkiewicz K, Nilsson P, Olsen MH, Rahn KH, Redon J, Rodicio J, Ruilope L, Schmieder RE, Struijker-Boudier HA, van Zwieten PA, Viigimaa M, Zanchetti A (2009) European Society of Hypertension. Reappraisal of European guidelines on hypertension management: a European Society of Hypertension Task Force document. J Hypertens 27:2121–2158
Güder G, Frantz S, Bauersachs J, Allolio B, Wanner C, Koller MT, Ertl G, Angermann CE, Störk S (2009) Reverse epidemiology in systolic and nonsystolic heart failure: cumulative prognostic benefit of classical cardiovascular risk factors. Circ Heart Fail 2:563–571
Williams SG, Jackson M, Ng LL, Barker D, Patwala A, Tan LB (2005) Exercise duration and peak systolic blood pressure are predictive of mortality in ambulatory patients with mild-moderate chronic heart failure. Cardiology 104:221–226
Lee TT, Chen J, Cohen DJ, Tsao L (2006) The association between blood pressure and mortality in patients with heart failure. Am Heart J 151:76–83
Raphael CE, Whinnett ZI, Davies JE, Fontana M, Ferenczi EA, Manisty CH, Mayet J, Francis DP (2009) Quantifying the paradoxical effect of higher systolic blood pressure on mortality in chronic heart failure. Heart 95:56–62
Kallistratos MS, Dritsas A, Laoutaris ID, Cokkinos DV (2008) Incremental value of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide over left ventricle ejection fraction and aerobic capacity for estimating prognosis in heart failure patients. J Heart Lung Transplant 27:1251–1256
Kallistratos MS, Dritsas A, Laoutaris ID, Cokkinos DV (2007) N-terminal prohormone brain natriuretic peptide as a marker for detecting low functional class patients and candidates for cardiac transplantation: linear correlation with exercise tolerance. J Heart Lung Transplant 26:516–521
Mancini DM, Eisen H, Kussmaul W, Mull R, Edmunds LH Jr, Wilson JR (1991) Value of peak exercise consumption for optimal timing of cardiac transplantation in ambulatory patients with heart failure. Circulation 83:778–786
Riley M, Northridge DB, Henderson E, Stanford CF, Nichols DP, Dargie HJ (1992) The use of an exponential protocol for bicycle and treadmill exercise testing in patients with chronic cardiac failure. Eur Heart J 13:1363–1367
Wu A, Smith A, Wieczorek S, Mather J, Duncan B, White C, McGill C (2003) Biological variation for N-terminal Pro and B-type natriuretic peptides and implications for therapeutic monitoring of patients with congestive heart failure. Am J Cardiol 92:628–631
Domanski MJ, Mitchell GF, Norman JE, Exner DV, Pitt B, Pfeffer MA (1999) Independent prognostic information provided by sphygmomanometrically determined pulse pressure and mean arterial pressure in patients with left ventricular dysfunction. J Am Coll Cardiol 33:951–958
Voors A, Petrie C, Petrie M (2005) Low pulse pressure is independently related to elevated natriuretic peptides and increased mortality in advanced chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J 26:1759–1764
Kostis JB, Davis BR, Cutler J, Grimm RH Jr, Berge KG, Cohen JD, Lacy CR, Perry HM Jr, Blaufox MD, Wassertheil-Smoller S, Black HR, Schron E, Berkson DM, Curb JD, Smith WM, McDonald R, Applegate WB (1997) Prevention of heart failure by antihypertensive drug treatment in older persons with isolated systolic hypertension. SHEP Cooperative Research Group. JAMA 278:212–216
Weber MA (1987) Cardiovascular outcomes of treating high blood pressure. Am Heart J 114:964–971
Messerli FH, Mancia G, Conti CR, Hewkin AC, Kupfer S, Champion A, Kolloch R, Benetos A, Pepine CJ (2006) Dogma disputed: can aggressively lowering blood pressure in hypertensive patients with coronary artery disease be dangerous? Ann Intern Med 144:884–893
Anand IS, Tam SW, Rector TS, Taylor AL, Sabolinski ML, Archambault WT, Adams KF, Olukotun AY, Worcel M, Cohn JN (2007) Influence of blood pressure on the effectiveness of a fixed-dose combination of isosorbide dinitrate and hydralazine in the African-American Heart Failure Trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 49:32–39
Jourdain P, Jondeau G, Funck F, Gueffet P, Le Helloco A, Donal E, Aupetit JF, Aumont MC, Galinier M, Eicher JC, Cohen-Solal A, Juillière Y (2007) Plasma brain natriuretic peptide-guided therapy to improve outcome in heart failure: the STARS-BNP Multicenter Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 49:1733–1739
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kallistratos, M.S., Poulimenos, L.E., Pavlidis, A.N. et al. Prognostic significance of blood pressure response to exercise in patients with systolic heart failure. Heart Vessels 27, 46–52 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-010-0115-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-010-0115-z