Abstract
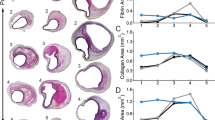
A major problem in the study of lesions of atherosclerosis is the difficulty of imaging noninvasively the lesions and following their progression in vivo. To address this problem, we have developed advanced magnetic resonance techniques to noninvasively and serially image advanced lesions of atherosclerosis in the rabbit abdominal aorta. Both lumen and wall were imaged with high resolution. Progression of disease, resulting in increase in lesion mass, decrease in arterial lumen, or stenosis, and intralesion complications, can be detected. Images acquired in vivo correlate with the fine structure of the lesions of atherosclerosis, including the fibrous cap, necrotic core, and lesion fissures, as verified by gross examination, dissection microscopy, and histology. The ability to noninvasively identify the features of atherosclerotic plaques, has significant implications for determining risks and benefits associated with different therapeutic approaches.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ross, R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: A perspective for the 1990s. Nature 362, 801–809 (1993).
Faggiotto, A., Ross, R. & Marker, L. Studies of hypercholesterolemia in the non-human primate. I. Changes that lead to fatty streak formation. Arteriosclerosis 4, 323–340 (1984).
Faggiotto, A. & Ross, R. Studies of hypercholesterolemia in the nonhuman primate. II. Fatty streak conversion to fibrous plaque. Arteriosclerosis 4, 341–356 (1984).
Masuda, J. & Ross, R. Atherogenesis during low level hypercholesterolemia in the nonhuman primate. I. Fatty streak formation. Arteriosclerosis 10, 164–177 (1990).
Masuda, J. & Ross, R. Atherogenesis during low level hypercholesterolemia in the nonhuman primate. II. Fatty streak conversion to fibrous plaque. Arteriosclerosis 10, 178–187 (1990).
Gerrity, R.G. The role of the monocyte in atherogenesis: I. Transition of blood-borne monocytes into foam cells in fatty lesions. Am J. Pathol. 103, 181–190 (1981).
Gerrity, R.G. The role of the monocyte in atherogenesis. II. Migration of foam cells from atherosclerotic lesions. Am J. Pathol 103, 191–200 (1981).
Stary, H.C. Evolution and progression of atherosclerotic lesions in coronary arteries of children and young adults. Arteriosclerosis 9 (suppl. I), 119132 (1989).
Davies, M.J. & Thomas, A. Thrombosis and acute coronary-artery lesions in sudden cardiac ischemic death. N. Engl. J. Med. 310, 1137–1140 (1984).
Topol, E.J. Textbook oflnterventional Cardiology, Vol. 1, 2nd Ed. (W. B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, 1994).
Fuster, V., Badimon, L., Badimon, J.J. & Chesebro, J.H. The pathogenesis of coronary artery disease and the acute coronary syndromes, part one. N. Engl. J. Med. 326, 242–250 (1992).
Fuster, V., Badimon, L., Badimon, J.J. & Chesebro, J.H. The pathogenesis of coronary artery disease and the acute coronary syndromes, part two N. Engl. J. Med. 326, 310–318 (1992).
Davies, M.J. & Woolf, N. Atherosclerosis: what is it and why does it occur? Br. Heart J. 69 (suppl.), S3S11 (1993).
Constantinides, P. Plaque fissures in human coronary thrombosis. J. atheroscler. Res. 6, 1–17 (1966).
Falk, E. Unstable angina with fatal outcome: dynamic coronary thrombosis leading to infarction and/or sudden death. Autopsy evidence of recurrent mural thrombosis with peripheral embolization culminating in total vascular occlusion. Circulation 71, 699–708 (1985).
Glagov, S., Zarins, C., Giddens, D.P. & Ku, D.N. Hemodynamics and atherosclerosis. Insights and perspectives gained from studies of human arteries. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 112, 1018–1031 (1988).
Forrester, J.S., Litvack, F. & Grundfest, W. Initiating events of acute coronary arterial occlusion. Annu. Rev. Med. 42, 35–45 (1991).
Mizuno, K. et al. Angioscopic evaluation of coronary-artery thrombi in acute coronary syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 326, 287–291 (1992).
Herfkens, R.J. et al. Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging of atherosclerotic disease. Radiology 148, 161–166 (1983).
Mohiaddin, R.H. & Longmore, D.B. MRI studies of atherosclerotic vascular disease: Structural evaluation and physiological measurements. Br. Med. Bull. 45, 968–990 (1989).
Pearlman, J.D., Southern, J.F. & Ackerman, J.L. Nuclear megnetic resonance microscopy of atheroma in human coronary arteries. Angiology 42, 726–733 (1991).
Vinitski, S., et al. Magnetic resonance chemical shift imaging and spectroscopy of atherosclerotic plaque. Invest. Radiol. 26, 703–714 (1991).
Maynor, C.H., Charles, H.C., Herfkens, R.J., Suddarth, S.A. & Johnson, G.A. Chemical shift imaging of atherosclerosis at 7.0 Tesla. Invest. Radiol. 24, 52–60 (1989).
Merickel, M.B. et al. Indentification and 3-D quantification of atherosclerosis using magnetic resonance imaging. Comput. Biol. Med. 18, 89–102 (1988).
Merickel, M.B. et al. Noninvasive quantitative evaluation of atherosclerosis using MRI and image analysis. Arterioscler. Thromb. 13, 1180–1186 (1993).
Pearlman, J.D. et al. High-resolution 1H NMR spectral signature from human atheroma. Magn. Reson. Med. 7, 262–279 (1988).
Matwiyoff, C., Gasparovic, C., Mazurchuk, R. & Matwiyoff, G. The line shapes of the water proton resonances of red blood cells containing carbonyl hemoglobin, deoxyhemoglobin, and methaemoglobin: Implications for the interpretation of proton MRI at field of 1.5T and below. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 8, 295–301 (1990).
Hayes, C., Mathis, C.M. & Yuan, C. Surface coil phased arrays for high resolution imaging of the carotid arteries. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging, in the press.
Manning, W.J., Li, W. & Edelman, R.R. A preliminary report comparing magnetic resonance coronary angiography with conventional angiography. N. Engl J. Med. 328, 828–832 (1993).
Edelman, R.R. & Warach, S. Magnetic resonance imaging. N. Engl. J. Med. 328, 708–716 (1993).
Edelman, R.R. & Warach, S. Magnetic resonance imaging. N. Engl. J. Med. 328, 785–791 (1993).
Mohiaddin, R.H. & Longmore, D.B. Functional aspects of cardiovascular nuclear magnetic resonance imaging. Techniques and application. Circulation 88, 264–281 (1993).
Gold, G.E. et al. Characterization of atherosclerosis with a 1.5T imaging system. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 3, 399–407 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skinner, M., Yuan, C., Mitsumori, L. et al. Serial magnetic resonance imaging of experimental atherosclerosis detects lesion fine structure, progression and complications in vivo. Nat Med 1, 69–73 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0195-69
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0195-69
This article is cited by
-
High-field magnetic resonance microscopy of aortic plaques in a mouse model of atherosclerosis
Magnetic Resonance Materials in Physics, Biology and Medicine (2023)
-
Molecular Imaging of Macrophages in Atherosclerosis
Current Cardiovascular Imaging Reports (2012)
-
Magnetic Resonance Angiography: Current Status in the Planning and Follow-Up of Endovascular Treatment in Lower-Limb Arterial Disease
CardioVascular and Interventional Radiology (2009)
-
Multicontrast-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of atherosclerotic plaques at 3.0 and 1.5 Tesla: ex-vivo comparison with histopathologic correlation
European Radiology (2007)