Summary
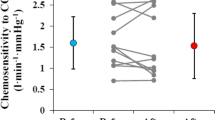
The present investigation examined the relationship between CO2 sensitivity [at rest (S R) and during exercise (S E)] and the ventilatory response to exercise in ten elderly (61–79 years) and ten younger (17–26 years) subjects. The gradient of the relationship between minute ventilation and CO2 production (Δ\(\dot V\) E/Δ\(\dot V\)CO2) of the elderly subjects was greater than that of the younger subjects [mean (SEM); 32.8 (1.6) vs 27.3 (0.4); P<0.01]. At rest, S R was lower for the elderly than for the younger group [10.77 (1.72) vs 16.95 (2.13) 1 · min−1 · kPa−1; 1.44 (0.23) vs 2.26 (0.28) 1 · min−1 · mmHg−1; P<0.05], but S E was not significantly different between the two groups [17.85 (2.49) vs 19.17 (1.62) l · min−1 · kPa−1; 2.38 (0.33) vs 2.56 (0.21) 1 · min−1 · mmHg−1]. There were significant correlations between both S R and S E, and Δ\(\dot V\) E/Δ\(\dot V\)CO2 (P<0.05; P<0.001) for the younger group, bot none for the elderly. The absence of a correlation for the elderly supports the suggestion that Δ\(\dot V\) E/Δ\(\dot V\)CO2 is not an appropriate index of the ventilatory response to exercise for elderly humans.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Black LF, Hyatt RE (1969) Maximal respiratory pressures: Normal values and relationship to age and sex. Am Rev Respir Dis 99:696–702
Brischetto MJ, Millman RP, Petersen DD, Silage DA, Pack AI (1984) Effect of ageing on ventilatory response to exercise and CO2. J Appl Physiol 56:1143–1150
Dubois A, Alcala R (1964) Airway resistance and mechanics of breathing in normal subjects 75 to 90 years of age. In: Cander L, Moyer JH (eds) Aging in the lung. Grime and Stratton, New York, p 156
D'Urzo AD, Chapman KR, Rebuck AS (1987) Effect of inspiratory resistive loading on control of ventilation during progressive respiratory exercise. J Appl Physiol 62:134–140
Frank NR, Mead J, Ferris BG (1957) The mechanical behaviour of the lungs in elderly persons. J Clin Invest 36: 1680–1687
Hey EN, Lloyd BB, Cunningham DJC, Jukes MGM, Bolton DPG (1966) Effects of various respiratory stimuli on the depth and frequency of breathing in man. Respir Physiol 1:193–205
Jacobi MS, Patil CP, Saunders KB (1987) Comparison of transient steady state and rebreathing methods of measuring the ventilatory response to carbon dioxide in man. J Physiol (Lond) 394:58P
Jones NL, Robertson DG, Kane JW (1979) Difference between end-tidal and arterial PCO 2 in exercise. J Appl Physiol 47:954–960
Kelley MA, Laufe MD, Millman RP, Peterson DD (1984) Ventilatory response to hypercapnia before and after athletic training. Respir Physiol 55:393–400
Kronenberg RS, Drage CW (1973) Attenuation of the ventilatory and heart rate responses to hypoxia and hypercapnia with aging in normal man. J Clin Invest 52:1812–1819
Martin BJ, Weil JV, Sparks KE, McCullough RE, Grover RF (1978) Exercise ventilation correlates positively with ventilatory chemoresponsiveness. J Appl Physiol 45:557–564
McConnell AK, Davies CTM (1992) A comparison of the ventilatory response to exercise of elderly and younger humans. J Gerontol 47:B137–141
McConnell AK, Semple ESG (1989) Ventilatory responses to CO2 at rest and during exercise in endurance trained and non-endurance trained humans. J Physiol (Lond) 412:39P
Mittman C, Edelman NH, Norris AH, Shock NW (1965) Relationship between chest wall and pulmonary compliance with age. J Appl Physiol 20:1211–1216
Pack AJ, Millman RP (1986) Changes in control of ventilation, awake and asleep, in the elderly. J Am Geriatr Soc 34:533–544
Patrick JM, Howard A (1972) Influence of age, sex, body size and lung size on the control and pattern of breathing during CO2 inhalation in Caucasians. Respir Physiol 16:337–350
Poon CS (1987) Ventilatory control in hypercapnia and exercise: optimization hypothesis. J Appl Physiol 62:2447–2459
Poon CS (1989) Effects of inspiratory elastic load on respiratory control in hypercapnia and exercise. J Appl Physiol 66:2400–2406
Read DJC (1967) A clinical method for assessing the ventilatory response to carbon dioxide. Aust Ann Med 16:20–32
Rebuck AS, Jones NL, Campbell EJM (1972) Ventilatory response to exercise and to CO2 rebreathing in normal subjects. Clin Sci 43:861–867
Robbins PA, Conway J, Cunningham DA, Khamnei S, Patterson DJ (1990) A comparison of indirect methods for continuous estimation of arterial PCO 2 in men. J Appl Physiol 68:1727–1731
Rubin S, Tack M, Cherniack NS (1982) Effect of aging on respiratory responses to CO2 and inspiratory resistive loads. J Gerontol 37:306–312
Thomas SG, Cunningham DA, Thompson J, Rechnitzer PA (1985) Exercise training and ventilation threshold in the elderly. J Appl Physiol 59:1472–1476
Weil JV, Byrne-Quinn E, Sodal IE, Kline JS, McCullough RE, Filley GF (1972) Augmentation of chemosensitivity during mild exercise in man. J Appl Physiol 33:813–819
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McConnell, A.K., Semple, E.S.G. & Davies, C.T.M. Ventilatory responses to exercise and carbon dioxide in elderly and younger humans. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 66, 332–337 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237778
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237778