Summary
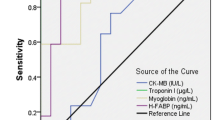
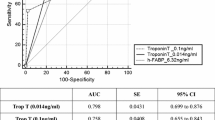
Heart fatty acid-binding protein (H-FABP) is supposed to be the most sensitive biomarker of early acute myocardial infarction (AMI). To evaluate the diagnostic value of H-FABP for AMI in the early stage, the plasma levels of H-FABP were measured by sandwich ELISA in 93 patients with suspected AMI at admission within 6h after onset of chest pain and 69 normal healthy subjects. The plasma concentrations of cardiac troponin-I (cTnI), creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB) and myoglobin (Mb) were assayed at the same time by using corpuscle chemiluminescence for those patients. The patients were classified as AMI group (n=32) and non-AMI group (n=61) retrospecitively. The diagnostic validity was evaluated in terms of sensitivity, specificity and receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve analysis. The results showed the cutoff value of H-FABP for AMI was 16.8 ng/ml, and it diagnostic sensitivity for AMI was 64.29% within 3h and 84.38% within 6 h after onset of chest pain, and the diagnostic specificity for non-AMI was 100% within 3 h and 91.8% within 6 h. H-FABP had higher sensitivity than that of cTnI and CK-MB at all time points (P<0.05), whereas there was no significant difference in specificity among the four markers. But the area under the ROC curve of H-FABP was significantly greater than that of cTnI, CK-MB and Mb within 3 h. These results revealed that H-FABP possessed high diagnostic sensitivity and specificity for AMI in early stage, especially within 3 h after onset of persistent angina pectoris. In conclusion, H-FABP can be used as a sensitive marker for AMI in the early stage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Swets J A. Measuring the accuracy of diagnostic systems. Science. 1988, 240: 1285
Wang L, Wu Y, Li L. Evaluation on usage of serum troponin-I, CK-MBmass and myoglobin measurements in diagnosing acute myocardial infarction. Hua Xi Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao (Chinese), 2000, 31(2): 239
McCord J, Nowak R M, Hudson M Pet al. The prognostic significance of serial myoglobin: troponin 1, and creatine kinase-MB measurements in patients evaluated in the emergency department for acute coronary syndrome. Ann Emerg Med, 2003, 42(3): 343
Nakata T, Hashimoto A, Hase Met al. Human heart-type fatty acid-binding protein as an early diagnostic and prognostic marker in acute coronary syndrome. Cardiology, 2003, 99(2): 96
Sanders G T, Schouten Y, DeWinter R Jet al. Evaluation of human heart type fatty acid-binding protein assay for carly detection of myocardial infarction. Clin Chem, 1998, 44: A132
Jan F C G, Kleine A H, van Nieuwenhoven F Aet al. Fatty-acid-binding protein as a plasma marker for the estimation of myocardial infarct size in humans. Br Heart J, 1994, 71: 135
Wu A H B, Apple F S, Giber W Bet al. National academy of clinical biochemistry standard of laboratory practice: recommendations for the use of cardiac markers in coronary artery diseases. Clin Chem, 1999, 45: 1104
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
CHEN Lili, female, born in 1974, Doctor in Charge
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lili, C., Xiaomei, G. & Fei, Y. Role of heart-type fatty acid binding protein in early detection of acute myocardial infarction in comparison with cTnI, CK-MB and myoglobin. Current Medical Science 24, 449–451 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02831105
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02831105