Abstract
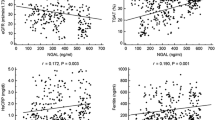
Plasma BNP and NT-proBNP are often regarded as interchangeable parameters in assessing heart failure (HF) severity and prognosis. Renal failure results in disproportionate increases of NT-proBNP and an increased NT-proBNP/BNP ratio. Low kidney function is therefore considered particularly when NT-proBNP is used to assess HF. The purpose of this study was to identify other conditions affecting the NT-proBNP/BNP ratio. We examined the NT-proBNP/BNP ratio, 26 other lab parameters, and clinical factors in 218 patients admitted to the HF ward. In addition to renal function, we also found significant correlations between the NT-proBNP/BNP ratio and inflammation as measured by orosomucoid (r = 0.525, p < 0.0001), CRP (r = 0.333, p < 0.0001), haptoglobulin (r = 0.201, p = 0.02), and alpha1-antitrypsin (r = 0.223, p = 0.01). Reverse correlation was found with transferrin (r = −0.323, p < 0.0001), albumin (r = −0.251, p = 0.003), and S–Fe (r = −0.205, p = 0.02), parameters known to decrease during inflammation. Inflammation increased levels of NT-proBNP more than BNP, resulting in an increased NT-proBNP/BNP ratio. Our findings indicate that NT-proBNP should be evaluated concomitantly with inflammatory status to avoid overestimation of HF severity.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BNP:
-
B-type natriuretic peptide
- CHF:
-
Chronic heart failure
- CV:
-
Coefficient of variation
- NT-proBNP:
-
N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide
- eGFR:
-
Estimated glomerular filtration rate
- HF:
-
Heart failure
References
Bayes-Genis A, Lloyd-Jones DM, van Kimmenade RR, Lainchbury JG, Richards AM, Ordonez-Llanos J, Santalo M, Pinto YM, Januzzi JL Jr (2007) Effect of body mass index on diagnostic and prognostic usefulness of amino-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in patients with acute dyspnea. Arch Intern Med 167:400–407
Bionda C, Bergerot C, Ardail D, Rodriguez-Lafrasse C, Rousson R (2006) Plasma BNP and NT-proBNP assays by automated immunoanalyzers: analytical and clinical study. Ann Clin Lab Sci 36:299–306
Bruins S, Fokkema MR, Romer JW, Dejongste MJ, van der Dijs FP, van den Ouweland JM, Muskiet FA (2004) High intraindividual variation of B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and amino-terminal proBNP in patients with stable chronic heart failure. Clin Chem 50:2052–2058
Chenevier-Gobeaux C, Delerme S, Allo JC, Arthaud M, Claessens YE, Ekindjian OG, Riou B, Ray P (2008) B-type natriuretic peptides for the diagnosis of congestive heart failure in dyspneic oldest-old patients. Clin Biochem 41:1049–1054
Chua G, Kang-Hoe L (2004) Marked elevations in N-terminal brain natriuretic peptide levels in septic shock. Crit Care 8:R248–R250
Daniels LB, Clopton P, Bhalla V, Krishnaswamy P, Nowak RM, McCord J, Hollander JE, Duc P, Omland T, Storrow AB, Abraham WT, Wu AH, Steg PG, Westheim A, Knudsen CW, Perez A, Kazanegra R, Herrmann HC, McCullough PA, Maisel AS (2006) How obesity affects the cut-points for B-type natriuretic peptide in the diagnosis of acute heart failure. Results from the Breathing Not Properly Multinational Study. Am Heart J 151:999–1005
Fonarow GC (2003) The acute decompensated heart failure national registry (ADHERE): opportunities to improve care of patients hospitalized with acute decompensated heart failure. Rev Cardiovasc Med 4(Suppl 7):S21–S30
Hoffmann U, Brueckmann M, Bertsch T, Wiessner M, Liebetrau C, Lang S, Haase KK, Borggrefe M, Huhle G (2005) Increased plasma levels of NT-proANP and NT-proBNP as markers of cardiac dysfunction in septic patients. Clin Lab 51:373–379
Hogenhuis J, Voors AA, Jaarsma T, Hoes AW, Hillege HL, Kragten JA, van Veldhuisen DJ (2007) Anaemia and renal dysfunction are independently associated with BNP and NT-proBNP levels in patients with heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail 9:787–794
Kavsak PA, Ko DT, Newman AM, Palomaki GE, Lustig V, MacRae AR, Jaffe AS (2007) Risk stratification for heart failure and death in an acute coronary syndrome population using inflammatory cytokines and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide. Clin Chem 53:2112–2118
Krauser DG, Lloyd-Jones DM, Chae CU, Cameron R, Anwaruddin S, Baggish AL, Chen A, Tung R, Januzzi JL Jr (2005) Effect of body mass index on natriuretic peptide levels in patients with acute congestive heart failure: a ProBNP investigation of dyspnea in the emergency department (PRIDE) substudy. Am Heart J 149:744–750
Luchner A, Hengstenberg C, Lowel H, Riegger GA, Schunkert H, Holmer S (2005) Effect of compensated renal dysfunction on approved heart failure markers: direct comparison of brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal pro-BNP. Hypertension 46:118–123
Luchner A, Hengstenberg C, Lowel H, Trawinski J, Baumann M, Riegger GA, Schunkert H, Holmer S (2002) N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide after myocardial infarction: a marker of cardio-renal function. Hypertension 39:99–104
Maisel A, Mueller C, Adams K Jr, Anker SD, Aspromonte N, Cleland JG, Cohen-Solal A, Dahlstrom U, DeMaria A, Di Somma S, Filippatos GS, Fonarow GC, Jourdain P, Komajda M, Liu PP, McDonagh T, McDonald K, Mebazaa A, Nieminen MS, Peacock WF, Tubaro M, Valle R, Vanderhyden M, Yancy CW, Zannad F, Braunwald E (2008) State of the art: using natriuretic peptide levels in clinical practice. Eur J Heart Fail 10:824–839
McCullough PA, Duc P, Omland T, McCord J, Nowak RM, Hollander JE, Herrmann HC, Steg PG, Westheim A, Knudsen CW, Storrow AB, Abraham WT, Lamba S, Wu AH, Perez A, Clopton P, Krishnaswamy P, Kazanegra R, Maisel AS (2003) B-type natriuretic peptide and renal function in the diagnosis of heart failure: an analysis from the Breathing Not Properly Multinational Study. Am J Kidney Dis 41:571–579
Meirovich YF, Veinot JP, de Bold ML, Haddad H, Davies RA, Masters RG, Hendry PJ, de Bold AJ (2008) Relationship between natriuretic peptides and inflammation: proteomic evidence obtained during acute cellular cardiac allograft rejection in humans. J Heart Lung Trans 27:31–37
Meyer B, Huelsmann M, Wexberg P, Delle Karth G, Berger R, Moertl D, Szekeres T, Pacher R, Heinz G (2007) N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide is an independent predictor of outcome in an unselected cohort of critically ill patients. Crit Care Med 35:2268–2273
O’Hanlon R, O’Shea P, Ledwidge M, O’Loughlin C, Lange S, Conlon C, Phelan D, Cunningham S, McDonald K (2007) The biologic variability of B-type natriuretic peptide and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide in stable heart failure patients. J Card Fail 13:50–55
Piechota M, Banach M, Irzmanski R, Misztal M, Rysz J, Barylski M, Piechota-Urbanska M, Kowalski J, Pawlicki L (2007) N-terminal brain natriuretic propeptide levels correlate with procalcitonin and C-reactive protein levels in septic patients. Cell Mol Biol Lett 12:162–175
Provan SA, Angel K, Odegard S, Mowinckel P, Atar D, Kvien TK (2008) The association between disease activity and NT-proBNP in 238 patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a 10-year longitudinal study. Arthritis Res Ther 10:R70
Roch A, Allardet-Servent J, Michelet P, Oddoze C, Forel JM, Barrau K, Loundou A, Perrin G, Auffray JP, Portugal H, Papazian L (2005) NH2 terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide plasma level as an early marker of prognosis and cardiac dysfunction in septic shock patients. Crit Care Med 33:1001–1007
Rudiger A, Fischler M, Harpes P, Gasser S, Hornemann T, von Eckardstein A, Maggiorini M (2008) In critically ill patients, B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal pro-BNP levels correlate with C-reactive protein values and leukocyte counts. Int J Cardiol 126:28–31
Rudiger A, Gasser S, Fischler M, Hornemann T, von Eckardstein A, Maggiorini M (2006) Comparable increase of B-type natriuretic peptide and amino-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide levels in patients with severe sepsis, septic shock, and acute heart failure. Crit Care Med 34:2140–2144
Solus J, Chung CP, Oeser A, Avalos I, Gebretsadik T, Shintani A, Raggi P, Sokka T, Pincus T, Stein CM (2008) Amino-terminal fragment of the prohormone brain-type natriuretic peptide in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 58:2662–2669
Taylor JA, Christenson RH, Rao K, Jorge M, Gottlieb SS (2006) B-type natriuretic peptide and N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide are depressed in obesity despite higher left ventricular end diastolic pressures. Am Heart J 152:1071–1076
Tello-Montoliu A, Marin F, Roldan V, Mainar L, Lopez MT, Sogorb F, Vicente V, Lip GY (2007) A multimarker risk stratification approach to non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome: implications of troponin T, CRP, NT pro-BNP and fibrin D-dimer levels. J Intern Med 262:651–658
Wang TJ, Larson MG, Levy D, Leip EP, Benjamin EJ, Wilson PW, Sutherland P, Omland T, Vasan RS (2002) Impact of age and sex on plasma natriuretic peptide levels in healthy adults. Am J Cardiol 90:254–258
Varpula M, Pulkki K, Karlsson S, Ruokonen E, Pettila V (2007) Predictive value of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in severe sepsis and septic shock. Crit Care Med 35:1277–1283
Vickery S, Price CP, John RI, Abbas NA, Webb MC, Kempson ME, Lamb EJ (2005) B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and amino-terminal proBNP in patients with CKD: relationship to renal function and left ventricular hypertrophy. Am J Kidney Dis 46:610–620
Wolff B, Haase D, Lazarus P, Machill K, Graf B, Lestin HG, Werner D (2007) Severe septic inflammation as a strong stimulus of myocardial NT-pro brain natriuretic peptide release. Int J Cardiol 122:131–136
Acknowledgments
The authors of this manuscript have certified that they comply with the Principles of Ethical Publishing in the International Journal of Cardiology. We would like to thank the Swedish Research Council (M.L.X.F., O.H.), Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation (M.L.X.F.), Swedish Cancer Society (O.H.), the Swedish Pain Foundation (O.H.), and the Department of Laboratory Medicine at Sahlgren’s University Hospital Foundation (O.H.) for grant support. We also acknowledge Max Pertzold for data analysis, and Hans Herlitz for recruiting patients from the Department of Renal Diseases.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jensen, J., Ma, LP., Fu, M.L.X. et al. Inflammation increases NT-proBNP and the NT-proBNP/BNP ratio. Clin Res Cardiol 99, 445–452 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-010-0140-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-010-0140-z