Abstract
Introduction
Obesity is an independent risk factor in the development of diabetes. Weight loss surgery is the most effective treatment of morbid obesity. This study examines the effect of gastric banding on metabolic profile in diabetics.
Methods
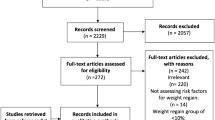
Between April 2003 and November 2007, 1,335 patients underwent laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. Metabolic profile was examined on a subset of 254 patients. Of these, 122 were diabetic. Data collection included body mass index, weight, blood pressure, HbA1c, fasting glucose, total serum cholesterol, triglyceride, and medications taken for blood pressure and diabetes both preoperatively and 1 year postoperatively.
Results
Comorbid conditions in the diabetic patients included hypercholesterolemia (49.3%), hypertriglyceridemia (53.8%) and hypertension (92%). In 1 year, mean BMI reduced from 52.9 kg/m2 to 41.5 kg/m2. Of the patients, 93.1% experienced an improvement in fasting glucose levels and 75.4% patients an improvement in HbA1c levels at the end of 1 year. All patients experienced a decrease in insulin requirements, and 36.6% were able to totally discontinue using it. Of the patients, 100% showed improvement in their triglyceride level, and 90.9% showed improvement in their total cholesterol level. The mean arterial pressure improved in 87.5% of the patients.
Conclusion
The metabolic syndrome associated with morbid obesity is difficult to adequately control with medication. Laparoscopic gastric banding can be considered a potentially curative treatment option in the management of this syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Must A, Spadano J, Coakley EH, Field AE, Colditz G, Dietz WH. The disease burden associated with overweight and obesity. JAMA. 1999;282(16):1523–9.
Chan JM, Rimm EB, Colditz GA, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC. Obesity, fat distribution, and weight gain as risk factors for clinical diabetes in men. Diabetes Care. 1994;17(9):961–9.
Kannel WB, McGee DL. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The Framingham study. JAMA. 1979;241(19):2035–8.
UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). Lancet. 1998;352(9131):854–65.
Turner RC, Cull CA, Frighi V, Holman RR. Glycemic control with diet, sulfonylurea, metformin, or insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: progressive requirement for multiple therapies (UKPDS 49). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. JAMA. 1999;281(21):2005–12.
Detournay B, Cros S, Charbonnel B, et al. Managing type 2 diabetes in France: the ECODIA survey. Diabetes Metab. 2000;26(5):363–9.
Newburgh L. Control of hyperglycaemia of obese ‘diabetics’ by weight reduction. Ann Intern Med. 1942;17:935–42.
Friedman MN, Sancetta AJ, Magovern GJ. The amelioration of diabetes mellitus following subtotal gastrectomy. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1955;100(2):201–4.
Buchwald H, Avidor Y, Braunwald E, et al. Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2004;292(14):1724–37.
Pontiroli AE, Pizzocri P, Librenti MC, et al. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding for the treatment of morbid (grade 3) obesity and its metabolic complications: a three-year study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87(8):3555–61.
Pontiroli AE, Folli F, Paganelli M, et al. Laparoscopic gastric banding prevents type 2 diabetes and arterial hypertension and induces their remission in morbid obesity: a 4-year case-controlled study. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(11):2703–9.
Dixon JB, O’Brien PE. Health outcomes of severely obese type 2 diabetic subjects 1 year after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. Diabetes Care. 2002;25(2):358–63.
Hubbard VS, Hall WH. Gastrointestinal surgery for severe obesity. Obes Surg. 1991;1(3):257–65.
1983 Metropolitan Height and Weight Tables. New York: Metropolitan Life Foundation. Statistical Bulletin. 1983;64(1):2–9.
Deitel M, Gawdat K, Melissas J. Reporting weight loss 2007. Obes Surg. 2007;17(5):565–8.
M Longmore IW, S Rajagopala. Oxford handbook of Clinical Medicine. 6 ed. 2004.
Management of Hypertension in Adults in Primary Care: NICE, June 2006.
Singhal R, Kitchen M, Ndirika S, Hunt K, Bridgwater S, Super P. The ‘Birmingham stitch’—avoiding slippage in laparoscopic gastric banding. Obes Surg. 2008 Apr;18(4):359–63. Epub 2008 Feb 20.
Ferchak CV, Meneghini LF. Obesity, bariatric surgery and type 2 diabetes–a systematic review. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2004;20(6):438–45.
Dixon JB, O’Brien PE, Playfair J, Chapman L, Schachter LM, Skinner S, et al. Adjustable gastric banding and conventional therapy for type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 23 Jan 2008;299(3):316–23.
Spivak H, Hewitt MF, Onn A, Half EE. Weight loss and improvement of obesity-related illness in 500 U.S. patients following laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding procedure. Am J Surg. 2005;189(1):27–32.
Ahroni JH, Montgomery KF, Watkins BM. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding: weight loss, co-morbidities, medication usage and quality of life at one year. Obes Surg. 2005;15(5):641–7.
Favretti F, Segato G, Ashton D, et al. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding in 1,791 consecutive obese patients: 12-year results. Obes Surg. 2007;17(2):168–75.
Myers JA, Sarker S, Shayani V. Treatment of massive super-obesity with laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2006;2(1):37–40; discussion 40.
Ballantyne GH, Farkas D, Laker S, Wasielewski A. Short-term changes in insulin resistance following weight loss surgery for morbid obesity: laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding versus laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Obes Surg. 2006;16(9):1189–97.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singhal, R., Kitchen, M., Bridgwater, S. et al. Metabolic Outcomes of Obese Diabetic Patients Following Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Banding. OBES SURG 18, 1400–1405 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-008-9500-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-008-9500-4