Abstract
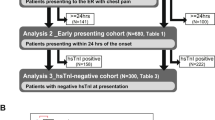
Early identification of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is important to guide therapy at a time when it is most likely to be of value. In addition, predicting future risk helps identify those most likely to benefit from ongoing therapy. Cardiac troponin T (cTnT) is useful for both purposes although cannot reliably rule out ACS until 12 hours after pain onset and does not fully define future risk. In this review article we summarize our previously published research, which assessed the value of myocyte injury, vascular inflammation, hemostatic, and neurohormonal markers in the early diagnosis of ACS and risk stratification of patients with ACS. In addition to cTnT, we measured heart fatty acid binding protein (H-FABP), glycogen phosphorylase-BB, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, myeloperoxidase, matrix metalloproteinase 9, pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A, D-dimer, soluble CD40 ligand, and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP). Of the 664 patients enrolled, 415 met inclusion criteria for the early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction (MI) analysis; 555 were included in the risk stratification analysis and were followed for 1 year from admission. In patients presenting <4 hours from pain onset, initial H-FABP had higher sensitivity for acute MI than cTnT (73% vs. 55%; P=0.043) but was of no benefit beyond 4 hours when compared to cTnT. On multivariate analysis, H-FABP, NT-proBNP, and peak cTnT were independent predictors of 1-year death/MI. Our research demonstrated that, in patients presenting within 4 hours from pain onset, H-FABP may improve detection of ACS. Measuring H-FABP and proBNP may help improve long-term risk stratification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thygesen K, Alpert JS, White HD. Universal definition of myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2007;28:2525–2538.
McCann CJ, Glover BM, Menown IBA, et al. Novel biomarkers in early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction compared with cardiac troponin T. Eur Heart J. 2008;29:2843–2850.
McCann CJ, Glover BM, Menown IBA, et al. Prognostic value of a multi-marker approach for patients presenting to hospital with acute chest pain. Am J Cardiol. 2009;103:22–28.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCann, C.J., Glover, B.M., Menown, I.B.A. et al. Investigation of a multimarker approach to the initial assessment of patients with acute chest pain. Adv Therapy 26, 531–534 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-009-0032-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-009-0032-7